15 Foods High in Cholesterol: What to Eat and Avoid

High cholesterol in your blood is associated with a number of medical problems, including heart disease and stroke. [1] Professional CCM. High cholesterol diseases. Cleveland Clinic. Published November 19, 2024 But cholesterol by itself is not bad. Cholesterol is necessary for your body to build cells and make vital hormones and vitamins necessary for life. Some cholesterol you consume in your diet, but your body also makes cholesterol in your liver. [2] What is Cholesterol? www.heart.org. Published October 14, 2024.
Cholesterol becomes a problem when you have too much of it. Maintaining healthy levels of cholesterol can reduce your risk of developing heart and vascular disease, and your diet is one way to help control these levels.
This article will discuss 15 foods to be mindful of when watching your cholesterol levels and some smart swaps you may want to choose instead.
Related: Heart‑Healthy Diet: Foods to Include and Avoid
What Is Cholesterol and Why Should You Care?
Cholesterol has a waxy consistency that the body uses to make cell membranes as well as hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and cortisol, among others. [3] Trevor Huff, Brandon Boyd, Ishwarlal Jialal Physiology, Cholesterol
It is also used in the synthesis of vitamin D and bile salts, which help the body absorb vitamins A, D, E, and K. [4] Di Ciaula A, Garruti G, Baccetto RL, et al. Bile Acid Physiology. Annals of Hepatology. 2017;16:S4-S14. doi:10.5604/01.3001.0010.5493 2017
HDL, LDL, and Triglycerides
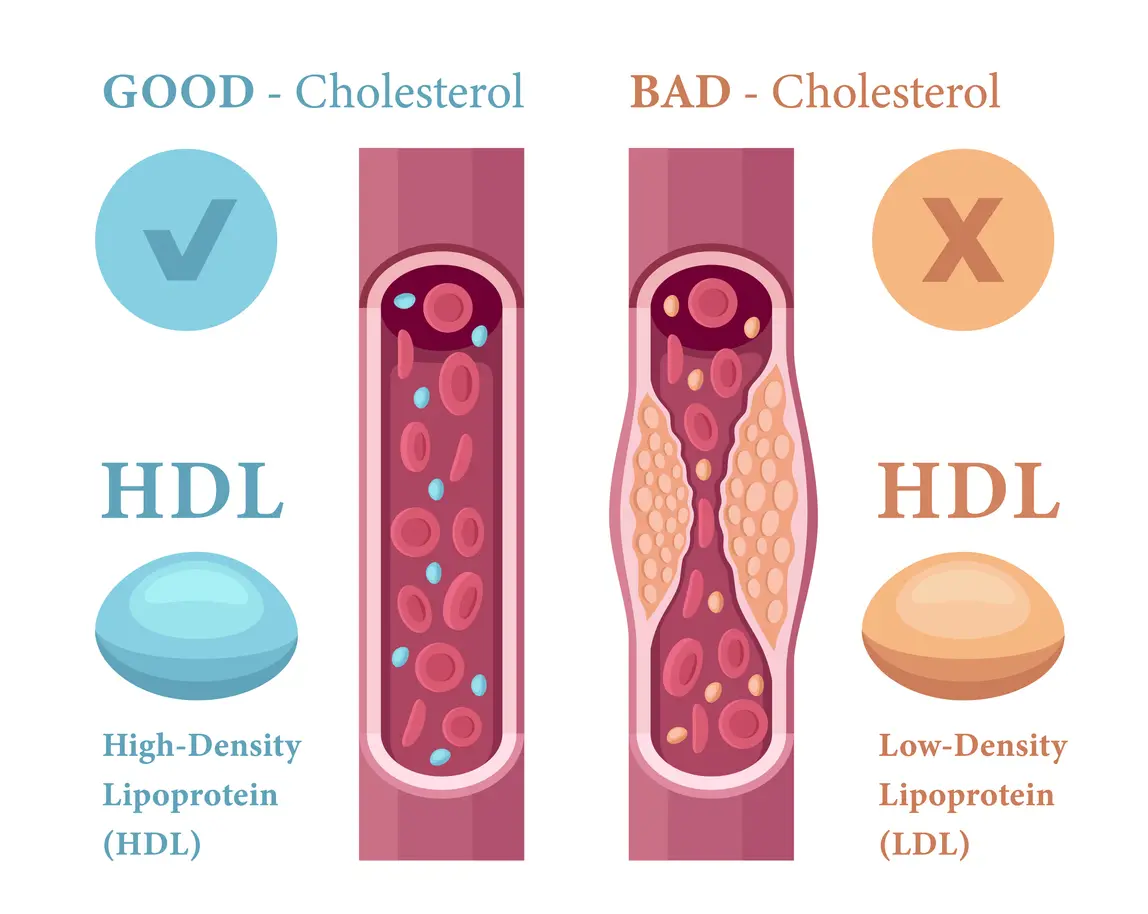
Cholesterol is a broader term for several particles, including high-density lipoprotein (HDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and triglycerides. These measures can also be called blood cholesterol.
HDL cholesterol is also referred to as “good” cholesterol. Healthy levels of this form of cholesterol can actually be protective against heart attacks and strokes. HDL can be thought of as a cleanup molecule carrying LDL cholesterol back to the liver, where the body can break it down and remove it. [5] HDL (Good), LDL (Bad) cholesterol and triglycerides. www.heart.org. Published October 14, 2024.
LDL cholesterol is sometimes thought of as “bad” cholesterol. Too much of this type of cholesterol can cause buildup in the arteries, which causes atherosclerosis. The buildup can cause heart attacks and strokes, among other health problems. [6] What is Blood Cholesterol? | NHLBI, NIH. NHLBI, NIH. Published April 17, 2024.
A third type of cholesterol molecule often monitored in bloodwork is triglycerides. These are the most common fats in the body and are responsible for storing excess energy that comes from your diet.
The Role of Saturated and Unsaturated Fats
There are two primary forms of dietary fats: saturated and unsaturated. These describe how the components of the fats are oriented. These factors are known as dietary cholesterol.
Saturated fats should make up less than 10% of your daily calories, ideally 5 to 6%, according to American Heart Association guidelines. Saturated fats are usually solid at room temperature and increase cholesterol levels. This type of fat is often found in meat, dairy, and tropical oils such as coconut. [7] Saturated fat. www.heart.org. Published March 10, 2025
Unsaturated fats are divided into monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Monounsaturated fats are found in many plants and plant-based oils. These can lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol. Polyunsaturated fats are further subdivided into Omega-6 and Omega-3 fatty acids.
These fatty acids are found in some plant-based oils as well as oily fish, seeds, and nuts. Omega-6 and Omega-3 fatty acids can decrease triglycerides, decrease LDL, increase HDL, and improve blood sugars. [8] Learn the facts about fat. Mayo Clinic.
Recommended Daily Limits
Previously, the American Heart Association (AHA) recommended keeping dietary cholesterol below 300 mg daily. The current guidelines recommend minimizing your cholesterol intake as much as possible while still maintaining a nutritious diet. [9] Here’s the latest on dietary cholesterol and how it fits in with a healthy diet. www.heart.org. Published September 5, 2023.
Related: Low Blood Pressure Diet: Foods To Increase Low BP
15 Foods High in Cholesterol
So, what foods should you watch out for? Here are 15 foods that are known to be high in cholesterol.
Foods to Eat in Moderation
The first group of foods we’ll discuss is those that should be eaten in moderation.
1. Eggs
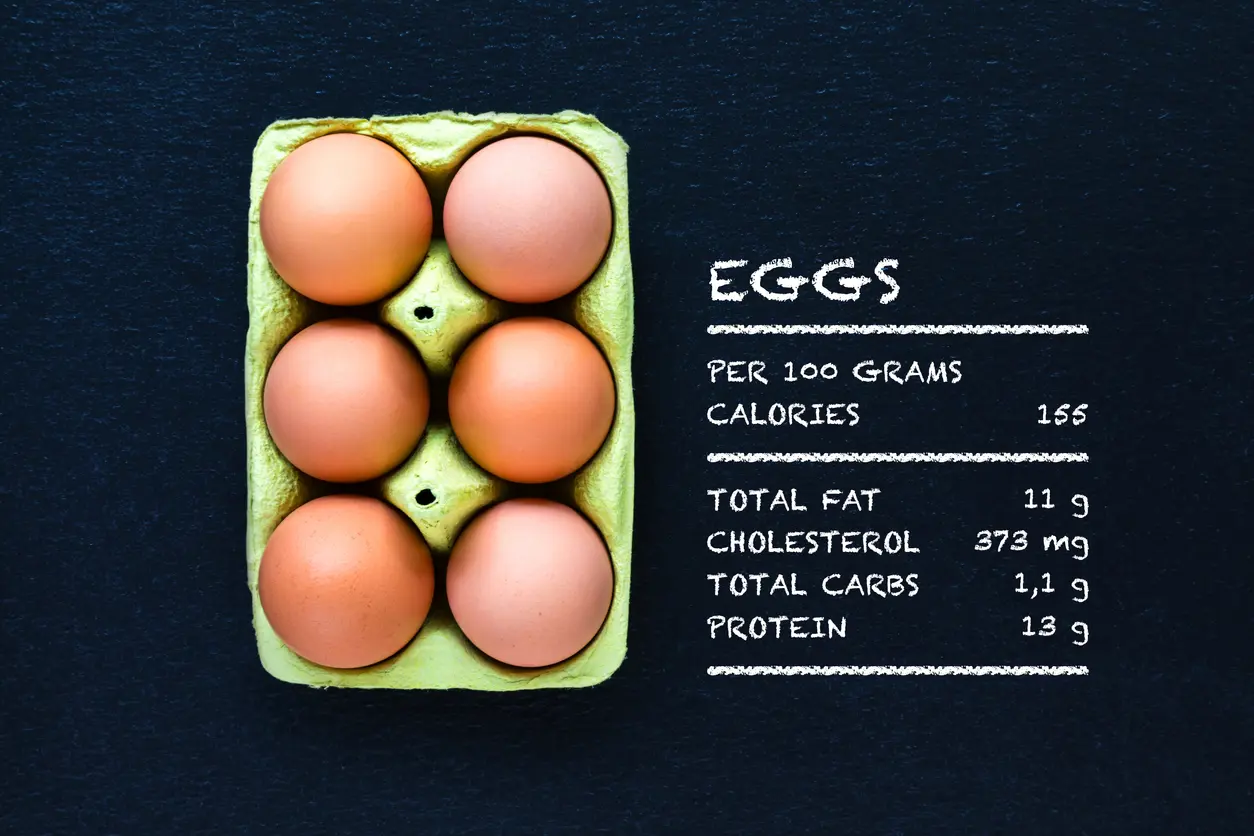
Eggs have been discussed with regard to cholesterol for quite some time. A large egg yolk contains around 186-275 mg of cholesterol. [10] Carson JAS, Lichtenstein AH, Anderson CAM, et al. Dietary cholesterol and cardiovascular risk: A science advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;141(3). doi:10.1161/cir.0000000000000743 2020, [11] Li MY, Chen JH, Chen C, Kang YN. Association between Egg Consumption and Cholesterol Concentration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2020;12(7):1995. doi:10.3390/nu12071995 2020 Though high in cholesterol, eggs are also a good source of protein and other nutrients.
Egg consumption, in moderation, may decrease your risk of developing other diseases. There are ways to prepare eggs to minimize excess cholesterol. For example, eating egg whites or cholesterol-free egg substitutes and preparing eggs without saturated fats, such as butter. [12] Eggs: Are they good or bad for my cholesterol? Mayo Clinic.
2. Shellfish
Shellfish such as shrimp are also fairly high in cholesterol. A serving of three ounces of shrimp contains around 161mg of cholesterol. Shrimp also contains higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, as well as antioxidants and other healthy nutrients. [13] Brianna Elliott, RD Is shrimp healthy? Nutrition, calories, and more. Healthline. Published November 27, 2024.
As with many foods, how shellfish is prepared plays a big role in how it contributes to health. Boiling or steaming shrimp is healthier than frying.
3. Cheese
Cheese is another food that has often been considered high in cholesterol. The amount of cholesterol in cheese depends on the type of cheese. For example, fat-free cheese may contain as little as 5 mg of cholesterol per serving, whereas cheddar contains around 131 mg per 1 cup serving. [14] How does cheese affect cholesterol levels? Published June 6, 2018.
The relationship between cheese and health risk is complicated, and studies have shown mixed results. [15] Feeney EL, O’Sullivan A, Nugent AP, et al. Patterns of dairy food intake, body composition and markers of metabolic health in Ireland: results from the National Adult Nutrition Survey. Nutrition and Diabetes. 2017;7(2):e243. doi:10.1038/nutd.2016.54 2017
4. Full-Fat Dairy (Yogurt, Milk)
Dairy products have multiple vitamins and nutrients, but full-fat dairy sources may be higher in saturated fats. [16] Schmidt KA, Cromer G, Burhans MS, et al. Impact of low-fat and full-fat dairy foods on fasting lipid profile and blood pressure: exploratory endpoints of a randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2021;114(3):882-892. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqab131
Dairy fat may not contribute significantly to fasting blood cholesterol levels, according to a 2021 study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. [17] Full-fat dairy foods and cardiovascular disease: Is there a connection? Mayo Clinic Press. Published January 30, 2025.
Low-fat or fat-free alternatives have less cholesterol than their full-fat counterparts.
5. Liver and Organ Meats
Liver and other organ meats can be a great source of nutrients such as iron, folate, and vitamin B12. However, these meats may also be high in cholesterol.
Beef brain contains 2,000 mg of cholesterol per 3.5-ounce serving, while liver contains 381 mg. [18] Daisy Coyle, APD Are organ meats healthy? Healthline. Published April 27, 2023.
Using lower cholesterol, lower-fat preparation methods may help lower the cholesterol content of these foods, which should be eaten in moderation.
6. Red Meat
Red meats are another higher cholesterol food that should be eaten in moderation. Beef, pork, and lamb are all higher in saturated fats. The cut of meat plays a role in the amount of cholesterol in these foods. [19] Harvard Health. 4 foods not to eat if you have high cholesterol. Harvard Health. Published June 22, 2023.
Lean and extra lean cuts of beef contain around 95 mg of cholesterol, while fattier cuts contain more. [20] Your guide to the leanest cuts of beef. Mayo Clinic.
Rinsing or draining meat after cooking can help cut down on the fat content.
7. Butter and Ghee
Butter is another food that has been linked to high cholesterol. Butter has a higher content of saturated fats. Ghee is a form of butter that has the proteins removed from it. Also known as clarified butter, this product is used in traditional Indian cooking. Some alternatives to butter include avocados, olive oil, yogurt, and applesauce. [21] McDermott A. How does butter affect my cholesterol levels? Healthline. Published August 26, 2024.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
While the foods listed above can be consumed in moderation, you should limit or avoid these other foods altogether.
8. Bacon
Many people find bacon delicious, but it is high in cholesterol and saturated fat. Uncooked bacon contains around 18.5 mg of cholesterol per slice. It also contains about 3.53 g of saturated fat per slice. [22] Villines Z. Bacon cholesterol and its impact on health. Published August 22, 2023.
Bacon is high in sodium, which can raise blood pressure, and it is high in nitrates that may increase the risk of gastric cancer. [23] Zhang FX, Miao Y, Ruan JG, et al. Association between Nitrite and Nitrate Intake and Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medical Science Monitor. 2019;25:1788-1799. doi:10.12659/msm.914621
The high levels of saturated fat in bacon may increase LDL cholesterol levels. There are several plant-based alternatives to bacon that are lower in saturated fats and offer a healthier option.
9. Sausage

Sausage is another food high in saturated fats and cholesterol. Like bacon, sausage is a processed meat with increased levels of sodium and saturated fat. Beef and pork sausage contain the highest amounts of cholesterol. [19] Harvard Health. 4 foods not to eat if you have high cholesterol. Harvard Health. Published June 22, 2023.
Sausage is high in sodium and nitrates. Chicken and turkey sausage alternatives may be lower in cholesterol, but are generally still higher in sodium and nitrates. There are also plant-based alternatives.
10. Fried Fast Food
Fried foods and fast foods are notoriously high in saturated fat and cholesterol. These foods are higher in calories than their baked, steamed, or poached counterparts. The amount of saturated fat and calories in these foods varies. [24] Rd KM. Why are fried foods bad for you? Healthline. Published June 7, 2023.
Trans fat content in oil can increase when the oil is heated or reheated. [25] Bhardwaj S, Passi SJ, Misra A, et al. Effect of heating/reheating of fats/oils, as used by Asian Indians, on trans fatty acid formation. Food Chemistry. 2016;212:663-670. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.06.021
Using alternative cooking methods such as baking, steaming, or air frying can decrease the fat and cholesterol content of these foods.
11. Processed Pastries
Processed foods often contain butter and shortening in large amounts. This can increase the saturated fat as well as the cholesterol in the foods. While the cholesterol levels in food may not directly correlate with the LDL cholesterol levels in blood, the increased saturated fats often do.
Baking with alternatives such as applesauce and bananas can lower the saturated fat and cholesterol levels in the foods. [19] Harvard Health. 4 foods not to eat if you have high cholesterol. Harvard Health. Published June 22, 2023.
12. Ice Cream
Ice cream is often high in both refined sugars and saturated fats. The amount of cholesterol and fat in ice cream depends on the flavor. Full-fat ice cream may be substituted with light or nonfat varieties for a healthier alternative. [26] Mph ZS. What to know about ice cream and cholesterol levels. Published November 30, 2023.
13. Chicken Skin
Chicken meat is often lean. However, chicken skin is another story. The skin of a chicken contains nearly 80% of its fat. Eating chicken without the skin, especially when prepared with an alternative to frying, can decrease the cholesterol and saturated fat content of your meal. [27] Veazey K. What to know about cholesterol levels in chicken. Published July 29, 2022.
14. Commercial Baked Goods With Trans Fats
Similar to processed pastries, commercial baked goods often contain butter, shortening, and other ingredients high in trans fats. Skipping the doughnuts and opting for alternatives such as nuts or fresh fruit gives you a healthier alternative. [28] Professional CCM. Cholesterol and nutrition. Cleveland Clinic. Published May 9, 2025.
15. Hydrogenated Margarine
Margarine is high in trans fat. This is especially true for margarine that contains hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated oils. Margarine contains 0.5 to 2 g of saturated fat per tablespoon. [29] Clinic C. Margarine or butter: the Heart-Healthiest spreads. Cleveland Clinic. Published April 22, 2025. Fortunately, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) banned partially hydrogenated oils from margarines, which improved the nutritional quality of this food. The trans fats in margarine are now naturally occurring rather than manmade. [30] Plain C. Margarines now nutritionally better than butter after hydrogenated oil ban - School of Public Health - University of Minnesota. School of Public Health. Published December 13, 2021
Heart-Healthy Eating Tips
We’ve discussed foods that may be best to eat in moderation or avoid, but let’s discuss other heart-healthy eating tips.
Eat More Fiber (Oats, Beans, Leafy Greens)
Foods high in soluble fiber, such as oatmeal and leafy greens, can decrease your LDL cholesterol. Other foods in this class include beans, apples, and Brussels sprouts. These foods lower your cholesterol by reducing the amount of dietary cholesterol that gets into your bloodstream. Aim for five to 10 grams per day. [31] Can eating certain foods help improve your cholesterol levels? Mayo Clinic.
Add Omega-3 Fats (Fatty Fish, Walnuts, Flaxseed)

A 2023 study in the Journal of the American Heart Association demonstrated that omega-3 fatty acids can decrease triglycerides and LDL cholesterol, which may help decrease your risk of having a cardiovascular event such as a stroke or heart attack. [32] Wang T, Zhang X, Zhou N, et al. Association between omega‐3 fatty acid intake and dyslipidemia: a Continuous Dose–Response Meta‐Analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2023;12(11). doi:10.1161/jaha.123.029512
Cook With Olive Oil Instead of Butter
Olive oil is high in omega fatty acids, which makes it a healthier alternative to butter and other oils higher in saturated fats. [33] Robertson R PhD. Omega-3-6-9 fatty acids: A complete overview. Healthline. Published May 19, 2023.
Read Food Labels for Trans Fat and Saturated Fat
Food labels contain useful information about the nutritional value of foods. If you’re looking to reduce your saturated and trans fat intake, reading the food labels can help you make healthier food choices.
Limit Sugar and Refined Carbs (They Also Affect Cholesterol!)
Sugar and refined carbohydrates can increase your triglyceride levels, which negatively impact your blood cholesterol. These foods cause rapid changes in blood sugar and insulin levels and may also contribute to the development of obesity and diabetes. [34] Adda Bjarnadottir, MS, RDN (Ice) Why refined carbs are bad for you. Healthline. Published April 21, 2023.
Summary/FAQs
Can I eat eggs if I have high cholesterol?
- Eggs contain a number of healthy nutrients and, in moderation, can be part of a healthy diet even in people with high cholesterol. There are studies that suggest an egg a day does not increase your risk of cardiovascular disease and may actually help prevent it. [35] Harvard Health Are eggs risky for heart health? Harvard Health. Published April 16, 2024.
Is all cholesterol bad?
- Cholesterol is necessary for overall health and is not bad by itself. Cholesterol becomes a concern when it is too high, especially LDL cholesterol. [1] Professional CCM. High cholesterol diseases. Cleveland Clinic. Published November 19, 2024
What is the worst food for cholesterol?
- There is no food that is the worst for cholesterol, but in general, foods that are higher in saturated fats are more likely to negatively impact your cholesterol.
If you’re looking for ways to lower your cholesterol naturally, consider downloading our Heart-Healthy Grocery Guide and newsletters for weekly nutrition tips.
Was this article helpful?
-
Professional CCM. High cholesterol diseases. Cleveland Clinic. Published November 19, 2024;
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/11918-cholesterol-high-cholesterol-diseases -
What is Cholesterol? www.heart.org. Published October 14, 2024.;
https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/cholesterol/about-cholesterol -
Physiology, Cholesterol; Trevor Huff, Brandon Boyd, Ishwarlal Jialal;
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470561/ -
Bile Acid Physiology. Annals of Hepatology. 2017;16:S4-S14. doi:10.5604/01.3001.0010.5493; Di Ciaula A, Garruti G, Baccetto RL, et al.; ( 2017 )
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29080336/ -
HDL (Good), LDL (Bad) cholesterol and triglycerides. www.heart.org. Published October 14, 2024. ;
https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/cholesterol/hdl-good-ldl-bad-cholesterol-and-triglycerides -
What is Blood Cholesterol? | NHLBI, NIH. NHLBI, NIH. Published April 17, 2024. ;
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/blood-cholesterol -
Saturated fat. www.heart.org. Published March 10, 2025;
https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/fats/saturated-fats -
Learn the facts about fat. Mayo Clinic.;
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/fat/art-20045550 -
Here’s the latest on dietary cholesterol and how it fits in with a healthy diet. www.heart.org. Published September 5, 2023.;
https://www.heart.org/en/news/2023/08/25/heres-the-latest-on-dietary-cholesterol-and-how-it-fits-in-with-a-healthy-diet -
Dietary cholesterol and cardiovascular risk: A science advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;141(3). doi:10.1161/cir.0000000000000743; Carson JAS, Lichtenstein AH, Anderson CAM, et al.; ( 2020 )
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31838890/ -
Association between Egg Consumption and Cholesterol Concentration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2020;12(7):1995. doi:10.3390/nu12071995; Li MY, Chen JH, Chen C, Kang YN.; ( 2020 )
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32635569/ -
Eggs: Are they good or bad for my cholesterol? Mayo Clinic.;
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-cholesterol/expert-answers/cholesterol/faq-20058468 -
Is shrimp healthy? Nutrition, calories, and more. Healthline. Published November 27, 2024. ; Brianna Elliott, RD;
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/is-shrimp-healthy -
How does cheese affect cholesterol levels? Published June 6, 2018. ;
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322044 -
Patterns of dairy food intake, body composition and markers of metabolic health in Ireland: results from the National Adult Nutrition Survey. Nutrition and Diabetes. 2017;7(2):e243. doi:10.1038/nutd.2016.54; Feeney EL, O’Sullivan A, Nugent AP, et al.; ( 2017 )
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28218736/ -
Impact of low-fat and full-fat dairy foods on fasting lipid profile and blood pressure: exploratory endpoints of a randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2021;114(3):882-892. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqab131; Schmidt KA, Cromer G, Burhans MS, et al. ;
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34258627/ -
Full-fat dairy foods and cardiovascular disease: Is there a connection? Mayo Clinic Press. Published January 30, 2025.;
https://mcpress.mayoclinic.org/dairy-health/full-fat-dairy-foods-and-cardiovascular-disease-is-there-a-connection/ -
Are organ meats healthy? Healthline. Published April 27, 2023.; Daisy Coyle, APD;
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/organ-meats -
Harvard Health. 4 foods not to eat if you have high cholesterol. Harvard Health. Published June 22, 2023.;
https://www.health.harvard.edu/heart-health/4-foods-not-to-eat-if-you-have-high-cholesterol -
Your guide to the leanest cuts of beef. Mayo Clinic.;
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/cuts-of-beef/art-20043833 -
McDermott A. How does butter affect my cholesterol levels? Healthline. Published August 26, 2024.;
https://www.healthline.com/health/butter-cholesterol -
Villines Z. Bacon cholesterol and its impact on health. Published August 22, 2023.;
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/bacon-cholesterol -
Association between Nitrite and Nitrate Intake and Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medical Science Monitor. 2019;25:1788-1799. doi:10.12659/msm.914621; Zhang FX, Miao Y, Ruan JG, et al. ;
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30850575/ -
Rd KM. Why are fried foods bad for you? Healthline. Published June 7, 2023.;
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/why-fried-foods-are-bad -
Effect of heating/reheating of fats/oils, as used by Asian Indians, on trans fatty acid formation. Food Chemistry. 2016;212:663-670. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.06.021; Bhardwaj S, Passi SJ, Misra A, et al.;
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27374582/ -
Mph ZS. What to know about ice cream and cholesterol levels. Published November 30, 2023.;
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/cholesterol-and-ice-cream -
Veazey K. What to know about cholesterol levels in chicken. Published July 29, 2022.;
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/cholesterol-in-chicken#by-part-of-the-chicken -
Professional CCM. Cholesterol and nutrition. Cleveland Clinic. Published May 9, 2025.;
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/16867-cholesterol--nutrition-tlc -
Clinic C. Margarine or butter: the Heart-Healthiest spreads. Cleveland Clinic. Published April 22, 2025. ;
https://health.clevelandclinic.org/margarine-or-butter-the-heart-healthiest-spreads-infographic -
Plain C. Margarines now nutritionally better than butter after hydrogenated oil ban - School of Public Health - University of Minnesota. School of Public Health. Published December 13, 2021;
https://www.sph.umn.edu/news/margarines-now-nutritionally-better-than-butter-after-hydrogenated-oil-ban/ -
Can eating certain foods help improve your cholesterol levels? Mayo Clinic.;
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-cholesterol/in-depth/cholesterol/art-20045192 -
Association between omega‐3 fatty acid intake and dyslipidemia: a Continuous Dose–Response Meta‐Analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2023;12(11). doi:10.1161/jaha.123.029512; Wang T, Zhang X, Zhou N, et al. ;
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37264945/ -
Robertson R PhD. Omega-3-6-9 fatty acids: A complete overview. Healthline. Published May 19, 2023.;
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/omega-3-6-9-overview -
Why refined carbs are bad for you. Healthline. Published April 21, 2023.; Adda Bjarnadottir, MS, RDN (Ice);
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/why-refined-carbs-are-bad -
Are eggs risky for heart health? Harvard Health. Published April 16, 2024.; Harvard Health;
https://www.health.harvard.edu/heart-health/are-eggs-risky-for-heart-health











